DIRECTED DEPOSITION OF QUANTUM DOTS BY CONVECTIVE SELF-ASSEMBLY
NANOSCIENCE

Lab: LPCNO
Duration: NanoX master Internship (8 months part-time in-lab immersion)
Latest starting date: 02/01/2025
Localisation: LPCNO (UMR 5215)
135 avenue de Rangueil
31077 TOULOUSE CEDEX 04 - FRANCE
Supervisors:
Giuseppe BONIELLO boniello@insa-toulouse.fr
Laurence RESSIER ressier@insa-toulouse.fr
This research master's degree project could be followed by a PhD
Work package:
Abstract / work package / illustration & legend
The ability to assemble nanoparticles into specific locations is fundamental for any application which requires
miniaturization in functional devices, such as sensing, plasmonics, anticounterfeiting, or micro- and nano-
electronics.
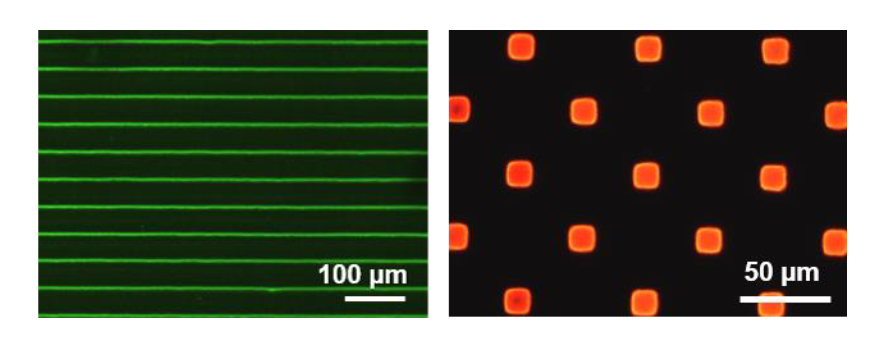
A suitable experimental method for particle deposition is Convective Self-Assembly (CSA). CSA involves the
translation of a meniscus of colloidal suspension on a solid substrate. A combination of convective flows induced
by evaporation and attractive capillary forces at the triple line between air, substrate and colloidal solution ensures
accumulation of particles in this zone and assists deposition [1]. This technique allows to assemble mono- and
multi-layers, 1-D and 2-D patterns of colloidal particles within a large range of sizes [2, 3]. While the assembly of
particles in aqueous solution is already addressed and understood, the behavior in non-polar solvents was just
recently taken on in our group. In this framework, the main objective of this internship will be to study the
deposition by CSA of quantum dots in non-polar solvents and in liquid crystals onto bare, functionalized and/or
patterned substrates. Different kinds of quantum dots will be considered in the experiments in terms of size, shape
and material.
The candidate will work in a clean room and will have access to various microfabrication techniques
(photolithography, nano-imprint lithography, laser lithography...) to create chemically, electrically and
topographically functionalized surfaces. She/he will deposit quantum dots by CSA technique; analyze the
assemblies by fluorescence microscopy, optical interferometry, atomic force microscopy (AFM), and scanning
electron microscopy (SEM); discuss with scientists performing numerical simulations (as a part of ongoing
collaborations with LGC – Toulouse) to address the research and understand the results. All the experimental set-
ups are available on site.
Depending on mutual appreciation, the internship can be followed by a PhD position (3 years) on the same topic.
References:
References:
[1] Malaquin, L.; Kraus, T.; Schmid, H.; Delamarche, E.; Wolf, H. Controlled Particle Placement through Convective
and Capillary Assembly. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11513−11521.
[2] Farcau, Cosmin, Neralagatta M. Sangeetha, Helena Moreira, Benoît Viallet, Jérémie Grisolia, Diana Ciuculescu-
Pradines, and Laurence Ressier. “High-Sensitivity Strain Gauge Based on a Single Wire of Gold Nanoparticles
Fabricated by Stop-and-Go Convective Self-Assembly.” ACS Nano 5, no. 9 (September 27, 2011): 7137–43.
https://doi.org/10.1021/nn201833y.
[3] Teulon, Lauryanne, Yannick Hallez, Simon Raffy, François Guerin, Etienne Palleau, and Laurence Ressier.
“Electrostatic Directed Assembly of Colloidal Microparticles Assisted by Convective Flow.” The Journal of Physical
Chemistry C 123, no. 1 (January 10, 2019): 783–90. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b08981.
Areas of expertise:
Nanoparticles, quantum dots, directed assembly, microfabrication, photolithography
Required skills for the internship:
The successful candidate is completing a MSc in physics, nanoscience, nanotechnology
and/or material science. Having experience in microfabrication and working in clean
room is a plus; in any case, training on experimental techniques will be carried out during
the internship. Moreover, she/he should be dynamic, autonomous, and taking initiative.
Good level of written and verbal English is required.
